Convolution Neural Network Part 2
Introduction
This project continues the talk from CNN Part 1, works with Convolutional Neural Networks and exploring its applications. We will mainly focus on Semantic Segmentation problems:
- Semantic Segmentationcluster areas of an image which belongs to the same object/label, and color with the same color section; We will implement semantic segmentation elaborately in CNN-Part2
- dataset: Oxford 17 Flowers Dataset 17 categories of flowers with 80 images in each set
- approach: Using Microsoft COCO Dataset, deeplabv3 especially as a finetuning base, and perform semantic segmentation

17 Flowers Dataset






Our task is simpily a binary semantic segmentation task, which classifies flower and its background.
Implementation
Jump to model Fine-tuning first to see Transfer Learning implementation and results
Utility Code
Helper Functions
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.io import loadmat
from PIL import Image
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
Data Processing
# Dataset helper function
def read_image(path):
im = cv2.imread(str(path))
return cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
def normalize(im):
"""Normalizes images with Imagenet stats."""
imagenet_stats = np.array([[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]])
return (im/255.0 - imagenet_stats[0])/imagenet_stats[1]
def denormalize(img):
imagenet_stats = np.array([[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]])
return img*imagenet_stats[1] + imagenet_stats[0]
class CUB(Dataset):
def __init__(self, files_path, split, train=True):
self.files_path = files_path
self.split = split
if train:
filenames = list(self.split['trn1'][0]) + list(self.split['trn2'][0]) + list(self.split['trn3'][0])
else:
# We only use `val1` for validation
filenames = self.split['val1'][0]
valid_filenames = []
for i in filenames:
img_name = 'image_%04d.jpg' % int(i)
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(files_path, 'jpg', img_name)) and \
os.path.exists(os.path.join(files_path, 'trimaps', img_name.replace('jpg', 'png'))):
valid_filenames.append(img_name)
self.valid_filenames = valid_filenames
self.num_files = len(valid_filenames)
def __len__(self):
return self.num_files
def __getitem__(self, index):
filename = self.valid_filenames[index]
# Load the image
path = os.path.join(self.files_path, 'jpg', filename)
x = read_image(path) # H*W*c
x = cv2.resize(x, (224,224))
x = normalize(x)
x = np.rollaxis(x, 2) # To meet torch's input specification(c*H*W)
# Load the segmentation mask
path = os.path.join(self.files_path, 'trimaps', filename.replace("jpg", "png"))
y = read_image(path)
y = cv2.resize(y, (224,224)) # H*W*c
return x, y
def initialize_loader(train_batch_size=64, val_batch_size=64):
split = loadmat("datasplits.mat")
train_dataset = CUB('./', split, train= True)
valid_dataset = CUB('./', split, train= False)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=train_batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4, drop_last=True)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=val_batch_size, num_workers=4)
return train_loader, valid_loader
Visualization
# Dataset helper function
def read_image(path):
im = cv2.imread(str(path))
return cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
def normalize(im):
"""Normalizes images with Imagenet stats."""
imagenet_stats = np.array([[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]])
return (im/255.0 - imagenet_stats[0])/imagenet_stats[1]
def denormalize(img):
imagenet_stats = np.array([[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]])
return img*imagenet_stats[1] + imagenet_stats[0]
class CUB(Dataset):
def __init__(self, files_path, split, train=True):
self.files_path = files_path
self.split = split
if train:
filenames = list(self.split['trn1'][0]) + list(self.split['trn2'][0]) + list(self.split['trn3'][0])
else:
# We only use `val1` for validation
filenames = self.split['val1'][0]
valid_filenames = []
for i in filenames:
img_name = 'image_%04d.jpg' % int(i)
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(files_path, 'jpg', img_name)) and \
os.path.exists(os.path.join(files_path, 'trimaps', img_name.replace('jpg', 'png'))):
valid_filenames.append(img_name)
self.valid_filenames = valid_filenames
self.num_files = len(valid_filenames)
def __len__(self):
return self.num_files
def __getitem__(self, index):
filename = self.valid_filenames[index]
# Load the image
path = os.path.join(self.files_path, 'jpg', filename)
x = read_image(path) # H*W*c
x = cv2.resize(x, (224,224))
x = normalize(x)
x = np.rollaxis(x, 2) # To meet torch's input specification(c*H*W)
# Load the segmentation mask
path = os.path.join(self.files_path, 'trimaps', filename.replace("jpg", "png"))
y = read_image(path)
y = cv2.resize(y, (224,224)) # H*W*c
return x, y
def initialize_loader(train_batch_size=64, val_batch_size=64):
split = loadmat("datasplits.mat")
train_dataset = CUB('./', split, train= True)
valid_dataset = CUB('./', split, train= False)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=train_batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4, drop_last=True)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=val_batch_size, num_workers=4)
return train_loader, valid_loader
Download dataset and initialize DataLoader
import os
if not os.path.exists("17flowers.tgz"):
print("Downloading flower dataset")
!wget https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/flowers/17/17flowers.tgz
!tar xvzf 17flowers.tgz
if not os.path.exists("trimaps.tgz"):
!wget https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/flowers/17/trimaps.tgz
!tar xvzf trimaps.tgz
if not os.path.exists("datasplits.mat"):
!wget https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/flowers/17/datasplits.mat
train_loader, valid_loader = initialize_loader()
visualize_dataset(train_loader)
Let’s visualize few examples with DataLoader

Load pre-trained model
# For further details, please refer to: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.05587.pds
model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.5.0', 'deeplabv3_resnet101', pretrained=True)
print(model)
Helper Functions for Training
def compute_loss(pred, gt):
loss = F.cross_entropy(pred, gt)
return loss
# from https://www.kaggle.com/iezepov/fast-iou-scoring-metric-in-pytorch-and-numpy
def iou_pytorch(outputs, labels):
SMOOTH = 1e-6
# You can comment out this line if you are passing tensors of equal shape
# But if you are passing output from UNet or something it will most probably
# be with the BATCH x 1 x H x W shape
outputs = torch.argmax(outputs, 1)
outputs = outputs.squeeze(1) # BATCH x 1 x H x W => BATCH x H x W
intersection = (outputs & labels).float().sum((1, 2)) # Will be zero if Truth=0 or Prediction=0
union = (outputs | labels).float().sum((1, 2)) # Will be zero if both are 0
iou = (intersection + SMOOTH) / (union + SMOOTH) # We smooth our devision to avoid 0/0
thresholded = torch.clamp(20 * (iou - 0.5), 0, 10).ceil() / 10 # This is equal to comparing with thresolds
return thresholded.mean() # Or thresholded.mean() if you are interested in average across the batch
def convert_to_binary(masks, thres=0.5):
binary_masks = ((masks[:, 0, :, :] == 128) & (masks[:, 1, :, :] == 0) & (masks[:, 2, :, :] == 0)) + 0.
return binary_masks.long()
def run_validation_step(args, epoch, model, loader, plotpath=None):
model.eval() # Change model to 'eval' mode (BN uses moving mean/var).
losses = []
ious = []
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (images, masks) in enumerate(loader):
permute_masks = masks.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # to match the input size: B, C, H, W
binary_masks = convert_to_binary(permute_masks)
if args.gpu:
images = images.cuda()
binary_masks = binary_masks.cuda()
output = model(images.float())
pred_seg_masks = output["out"]
output_predictions = pred_seg_masks[0].argmax(0)
loss = compute_loss(pred_seg_masks, binary_masks)
iou = iou_pytorch(pred_seg_masks, binary_masks)
losses.append(loss.data.item())
ious.append(iou.data.item())
val_loss = np.mean(losses)
val_iou = np.mean(ious)
if plotpath:
plot_prediction(args, model, False, index_list=[0], plotpath=plotpath, title='Val_%d' % epoch)
return val_loss, val_iou
Fine-tuning Model
For this task, we want to fine-tune only the last layer in our downloaded deeplabv3. We do this by keeping track of weights we want to update in learned_parameters.
Use the PyTorch utility Model.named_parameters(), which returns an iterator over all the weight matrices of the model.
The last layer weights have names prefix classifier.4. We will select the corresponding weights then passing them to learned_parameters.
Complete the train function in Part C of the notebook by adding 2-3 lines of code where indicated.
def train(args, model):
# Set the maximum number of threads to prevent crash in Teaching Labs
torch.set_num_threads(5)
# Numpy random seed
np.random.seed(args.seed)
# Save directory
# Create the outputs folder if not created already
save_dir = "outputs/" + args.experiment_name
if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
learned_parameters = []
# We only learn the last layer and freeze all the other weights
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if name.startswith("classifier.4"):
learned_parameters.append(param)
# Adam only updates learned_parameters
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(learned_parameters, lr=args.learn_rate)
train_loader, valid_loader = initialize_loader(args.train_batch_size, args.val_batch_size)
print("Train set: {}, Test set: {}".format(
train_loader.dataset.num_files, valid_loader.dataset.num_files))
print("Beginning training ...")
if args.gpu:
model.cuda()
start = time.time()
trn_losses = []
val_losses = []
val_ious = []
best_iou = None
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# Train the Model
model.train() # Change model to 'train' mode
start_tr = time.time()
losses = []
for i, (images, masks) in enumerate(train_loader):
permute_masks = masks.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # to match the input size: B, C, H, W
binary_masks = convert_to_binary(permute_masks) # B, H, W
if args.gpu:
images = images.cuda()
binary_masks = binary_masks.cuda()
# Forward + Backward + Optimize
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(images.float())
pred_seg_masks = output["out"]
_, pred_labels = torch.max(pred_seg_masks, 1, keepdim=True)
loss = compute_loss(pred_seg_masks, binary_masks)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.data.item())
# plot training images
if args.plot:
plot_prediction(args, model, True, index_list=[0], plotpath=save_dir+'/train_%d.png' % epoch, title='Train_%d' % epoch)
# plot training images
trn_loss = np.mean(losses)
trn_losses.append(trn_loss)
time_elapsed = time.time() - start_tr
print('Epoch [%d/%d], Loss: %.4f, Time (s): %d' % (
epoch+1, args.epochs, trn_loss, time_elapsed))
# Evaluate the model
start_val = time.time()
val_loss, val_iou = run_validation_step(args,
epoch,
model,
valid_loader,
save_dir+'/val_%d.png' % epoch)
if val_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = val_iou
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_dir, args.checkpoint_name + '-best.ckpt'))
time_elapsed = time.time() - start_val
print('Epoch [%d/%d], Loss: %.4f, mIOU: %.4f, Validation time (s): %d' % (
epoch+1, args.epochs, val_loss, val_iou, time_elapsed))
val_losses.append(val_loss)
val_ious.append(val_iou)
# Plot training curve
plt.figure()
plt.plot(trn_losses, "ro-", label="Train")
plt.plot(val_losses, "go-", label="Validation")
plt.legend()
plt.title("Loss")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.savefig(save_dir+"/training_curve.png")
# Plot validation iou curve
plt.figure()
plt.plot(val_ious, "ro-", label="mIOU")
plt.legend()
plt.title("mIOU")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.savefig(save_dir+"/val_iou_curve.png")
print('Saving model...')
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_dir, args.checkpoint_name + '-{}-last.ckpt'.format(args.epochs)))
print('Best model achieves mIOU: %.4f' % best_iou)
For fine-tuning we also want to
- use
Model.requires_grad_()to prevent back-prop through all the layers that should be frozen - replace the last layer with a new
nn.Conv2dwith appropriate input output channels and kernel sizes. Since we are performing binary segmentation for this assignment, this new layer should have 2 output channels.
class AttrDict(dict):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(AttrDict, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.__dict__ = self
args = AttrDict()
#You can play with the hyperparameters here, but to finish the assignment,
#there is no need to tune the hyperparameters here.
args_dict = {
'gpu':True,
'checkpoint_name':"finetune-segmentation",
'learn_rate':0.05,
'train_batch_size':128,
'val_batch_size': 256,
'epochs':10,
'seed':0,
'plot':True,
'experiment_name': 'finetune-segmentation',
}
args.update(args_dict)
#Truncate the last layer and replace it with the new one.
#To avoid `CUDA out of memory` error, you might find it useful (sometimes required)
# to set the `requires_grad`=False for some layers
model.requires_grad_(False)
model._modules['classifier'][4] = nn.Conv2d(256, 2, (3, 3))
# Clear the cache in GPU
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
train(args, model)
We can see that the training result is generalized really fast with IOU(Intersection Over Union) increasing
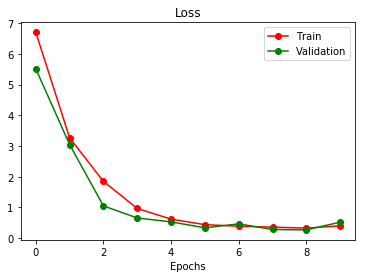
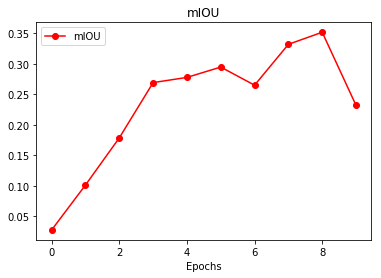
Visual Results
plot_prediction(args, model, is_train=True, index_list=[0, 1, 2, 3])
plot_prediction(args, model, is_train=False, index_list=[0, 1, 2, 3])






